Before we talk about how to reverse diabetes, let’s first understand about type 2 diabetes and how it affects your body?
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a group of disorders characterized by high blood glucose concentrations resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action or both.
In other words, diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot use the insulin effectively it produces. Insulin is a hormone produce by the pancreas that regulates the blood glucose levels. And sometimes your body does not make enough insulin or does not use it well. In turn, this glucose stays in your blood and does not reach your body cells and having too much glucose in your blood for longer period can cause health problems.
Do you know what is prediabetes? Understanding Pre-diabetes and insulin resistance
Types of Diabetes:
T1DM:
T1DM stands for Type 1 diabetes mellitus. The primary defect of this diabetes is pancreatic beta cell destruction, usually leading to absolute insulin deficiency. It is also known as insulin-dependent. It is usually diagnosed in children, teenagers, and young adults which is why it is known as juvenile or childhood-onset diabetes.
Furthermore, if you have T1DM, then you’ll need to take insulin every day to survive as neither its cause nor the means to prevent it are known yet.
Symptoms of T1DM:
It includes following symptoms:
- Excessive excretion of urine (polyuria)
- Excessive thirst (polydipsia)
- Constant hunger
- Weight loss
- Vision changes
- Fatigue.
T2DM:
T2DM stands for Type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this, the body does not produce enough insulin or does not use it properly (insulin resistance) then type 2 diabetes is likely to develop. It is also known as non-insulin-dependent, or adult-onset results from the body’s ineffective use of insulin.
About 90-95% of people with diabetes have type 2 diabetes mellitus. It can be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle changes such as losing weight, eating healthy food, and being active.
Symptoms of T2DM:
The symptoms of T2DM are almost similar to those of T1DM but these are often less marked. As a result, the diagnosis of disease may be delayed for years even after its onset. This is most likely to be diagnosed after complications have already arisen.
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM):
Gestational diabetes is diabetes whose diagnosis happens for the first time during pregnancy (gestation period). It affects how your cells use blood glucose and high blood sugar can affect your pregnancy and your baby’s health.
In women with gestational diabetes, blood sugar usually returns to normal soon after delivery. But if you’ve had gestational diabetes, you have a higher risk of getting type 2 diabetes. Thus, regular checkup is necessary to avoid the risk of developing diabetes.
Symptoms of GDM:
For most women, gestational diabetes doesn’t cause noticeable signs or symptoms. Increased thirst and more-frequent urination are possible symptoms.
Screening/risk factors of diabetes:
Screening for diabetes should be mandatory in all adults who are overweight and who have one or more additional risk factors for T2DM. In those without these risk factors, testing should begin at age 45 years. If tests are normal, testing shall be done at 3-year intervals. A1C test, Fasting Prandial Glucose, or 2-h Oral Glucose Tolerance Test can be used to test for either prediabetes or diabetes.
Additional risk factors for diabetes are the following:
- Physical inactivity
- First-degree relative with diabetes
- Members of a high-risk population (African Americans, Latino, Native American, Asian American, and Pacific Islander)
- Women who have delivered a baby weighing more than 9 lb or 4 kg or have been diagnosed with GDM
- Hypertensive (blood pressure 140/90 mm Hg or taking medication for hypertension)
- Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Other clinical condition associated with insulin resistance such as severe obesity, acanthosis nigricans [gray-brown skin pigmentations]).
- History of Cardiovascular disease.
Diagnostic criteria of diabetes:
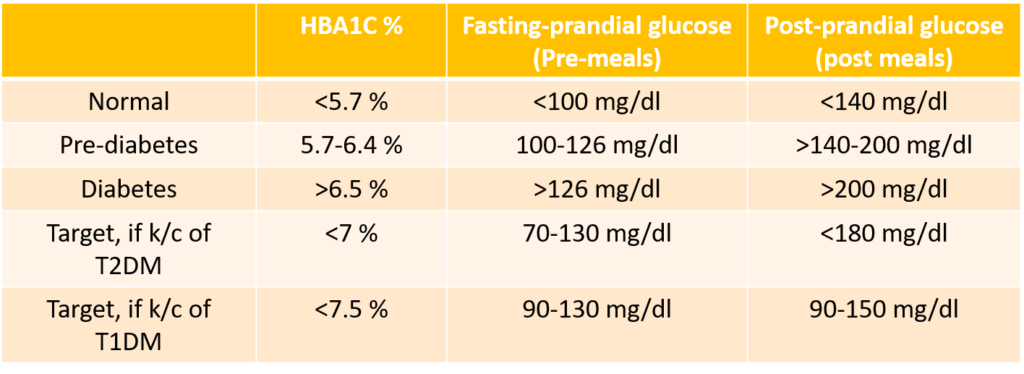
Let’s understand how can we reverse diabetes and control the same without medications:
There are so many research related to diabetes and how can you reverse it for good. As reversal can imply a permanent cure, a more apt term for this is diabetes remission. The complete cure is not found yet but putting your diabetes into remission can help. Yes, it may be possible to put your type 2 diabetes into remission. But this concept is not applicable on Type 1 diabetes. Researches are currently in progress on remission for type 1 diabetes as well but no effective results have come so far.
Do you know what Diabetes remission is? No, then let’s talk about it. Diabetes remission means that your blood sugar levels are below the diabetes range (complete remission) or in pre-diabetes range (partial remission), usually without you needing to take any diabetes medication for at least 6 months.

Source: https://www.bmj.com/content/374/bmj.n1449
You must be wondering that how people with type 2 diabetes may be able to put their diabetes into remission?
It is possible to put your diabetes into remission. Some people have lost a significant amount of weight and put their diabetes into remission through lifestyle and diet changes or by having weight loss surgery called bariatric surgery. But we, here at Fitpiq, prefer the most natural and healthy way to put your diabetes into remission.
Healthy lifestyle includes:
1) healthy weight/lose healthy weight
2) mindful eating
3) complete smoking cessation
4) alcohol in moderation
5) practice meditation
Lose extra weight:
The primary means by which people with type 2 diabetes achieve remission is by losing significant amounts of weight. For instance, if you are obese, then your diabetes is more likely to go into remission if you lose a significant amount of weight (let’s say 15kg) as quickly and safely as possible following your diagnosis.
Research shows that losing just 5%-10% of your body weight can have huge benefits for your health. Furthermore, losing weight and the fat around these organs allows them to work properly again which can put your diabetes into remission.
There are also other benefits of losing weight such as:
- Reducing your risk of developing complications from diabetes
- Improved blood sugar levels
- Reducing medications
- Lowering cholesterol levels
- Helps you to sleep better
Exercise:
People that have type 2 diabetes are most likely to be overweight or obese. This leads to fat building up around vital organs such as the pancreas and liver which causes them to not work as effectively and results in diabetes.
A exercise routine for at least 45 minutes of moderate intensity i.e. 5 to 6 days a week is very effective for your weight loss. Additionally, you can also opt for a daily step count challenge. This helps you in burning calories and reducing fat in your body. It also reduces insulin resistance, which brings your blood sugar under control.
How can you start:
- First step is choose something that you can stick to for longer period. If you choose something that you are not comfortable with, then you will most likely to get stray off the path.
- Always start with small changes and can increase it gradually as you start to develop strength. For example, you can park your vehicle farther from the door, take the stairs, go for brisk walking, do yard work, or walk the dog.
- Set a goal in your mind. For example, walk a mile every day for a month or yoga every weekend for 30 minutes.

Diet:
The low carb and low glycemic index diet is the most effective way to go into diabetes remission.
Low Carbohydrate diet:
Low-carbohydrate diets may seem to be a logical approach to lowering postprandial glucose. However, foods that contain carbohydrates (whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, and low-fat milk) are excellent sources of vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber, and energy.
A low-carb diet is one that limits carbohydrates, primarily found in sugary foods, refined pasta, and bread. Instead of eating simple carbs, this focuses on complex carbs, protein-rich whole foods, fruits and vegetables.
- Complex carbohydrates includes whole grains such as oats, wheat and millets such as ragi, jowar, bajra, etc.
- Protein rich foods include milk and milk products, pulses and legumes, eggs, lean meat, fish, poultry, etc.
- Low glycemic index fruits such as cherries, apple, orange, plums, pears, etc.
- Low glycemic index vegetables such as peas, onions, cabbage, beans, tomatoes, cucumber, bottle gourd, bitter gourd, ivy gourd, etc.
What is glycemic index? It shows the effect different foods have on the blood sugar levels.

Smoking cessation:
Smoking tends to increase the inflammation in the body. It also causes oxidative stress, a condition that occurs as chemicals from cigarette smoke combine with oxygen in the body. This causes damage to cells. And both inflammation and oxidative stress may be related to an increased risk of diabetes. Smoking is associated with a higher risk of abdominal obesity, or belly fat.
What is the relation between smoking and diabetes?
When people with type 2 diabetes are exposed to high levels of nicotine, insulin is less effective. People with diabetes who smoke need larger doses of insulin to control their blood sugar. So, complete smoking cessation is necessary for the insulin to start working better to lower blood glucose levels.

Meditation:
When we are in stress, then we tend to have higher cortisol levels which in turn increases insulin resistance. This stress also makes you to make wrong choices, for example, eating at night. This is particularly bad for diabetics, because there is a natural five-minute spike in growth hormone at 3:00 a.m.
This leads to a temporary increase in insulin resistance and subsequent higher blood sugar. So it’s very important to control stress and anxiety when treating diabetes.
Meditation will help people to relax and gives you some fresh perspective for dealing with stress. It can help by decreasing stress and regulating sleep patterns, so the person is sleeping through the night and not eating at midnight because of stress or anxiety.

Is the diabetes remission permanent?
Remission is not permanent but you can maintain it for longer periods with your active lifestyle, healthy weight and diet. It is always possible that your blood sugar levels could come back into the diabetes range. Thus, you need to keep an eye on your weight, and if you starts to gain weight again, then you can ask for extra support from experts to adjust your eating pattern and activity levels.
Can anyone put diabetes into remission phase?
It has been seen through several researches that the longer you have had type 2 diabetes, the more difficult it is to reach remission. As longer the time you have diabetes, the beta cells in the pancreas may lose their ability to produce insulin. And after a certain duration, it may be impossible to restore normal insulin production. Researchers suggest that diabetes remission is possible for some people out to ten years following diagnosis, though the DiRECT remission study only included people who had diabetes for six years or fewer.
What to keep in mind when you are in remission?
When you are remission, regular check-ups are mandatory as there are high chances that you may go back into the diabetes range. Test such as A1C test, fasting glucose and post prandial glucose test shall be done once in every 6 months.
If you are struggling shedding weight. You can talk to us by taking this assessment: Click here
For more information click here

