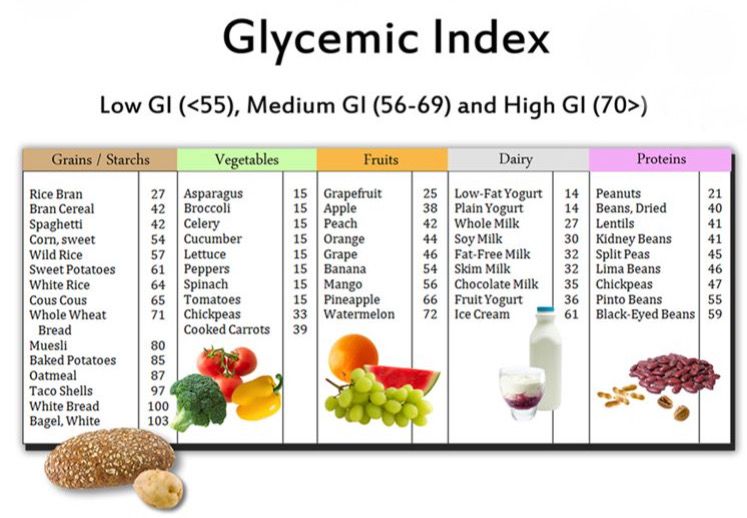
The glycemic index is a scale that ranks the number of carbohydrates in foods from zero to 100, indicating how quickly a food causes a person’s blood sugar to rise.
Foods high on the glycemic index (GI) can cause harmful blood sugar spikes in people with diabetes. Also High GI foods make it more challenging for a person to maintain a healthy weight. This is why some people with diabetes use GI to plan their meals.
Undoubtedly a nutritious, balanced diet includes a wide range of foods, so a person is not limited to consuming just low GI foods. However, knowing where a specific food rests on the GI can help a person make healthful choices.
Basically in this article, you will learn more about Glycemic index, and also not only about high but low GI foods.
What is Glycemic Index ?

The GI provides information about how the body digests carbohydrates using a scoring system of zero to 100. Pure sugar has a score of 100. Nutrition experts used to classify carbohydrates as either complex or simple. For example, table sugar is a simple carbohydrate, while beans and grains are complex carbohydrates.
Definition –
Glycemic Index (GI) is an important term often related to foods or diets prescribed for diabetics. GI is defined as the area under the blood glucose response curve for a specific food, expressed as a percentage of the area after taking the same amount of carbohydrates as glucose.
In simple words, it implies to what extent the blood glucose can rise after eating a particular carbohydrate diet, and these responses can differ from one carbohydrate source to the other. Foods with a low GI cause less of a spike in post meal blood glucose than those with a high GI. So much so that the response of blood glucose to the same carbohydrate food can vary if prepared in two different ways or given in two different forms.
For example, a pureed apple can cause a greater increase in GI or blood glucose rise as compared to when an apple is eaten raw as such.
The higher a food’s GI is, the more rapidly it elevates blood glucose. A high GI food can cause blood sugar spikes, followed by rapid declines in blood sugar. As blood sugar declines, a person may feel hungry. Eating only high GI foods can cause a person to overeat since they will quickly feel hungry again after eating.
Eating a diet with a low average GI may reduce a persons risk of developing diabetes and heart disease. In people who already have chronic conditions, a low GI diet may reduce the risk of complications and prevent blood glucose spikes.
Glycemic Index Score –

The GI scores are as follows:
- low GI foods: 55 or less
- medium GI foods: 56–69
- high GI foods: 70 or above
Some studies suggest that average dietary GI score of 45 may offer the most significant health benefits. This does not mean that a person can only eat foods with a GI score of 45 or lower. Rather, a person should balance their intake of higher GI foods by eating foods with a lower GI.
It is important to note that the GI of a specific food is an estimate. Several factors can affect the GI of a given food:
- Cooking tends to raise GI – The same type of pasta will have a lower GI if it is raw than it will if a person cooks it to the point of softness.
- Processing typically raises GI – For example, fruit juice typically has a higher GI than whole fruit.
- Riper foods usually have a higher GI – The GI of a banana, for example, will get higher as the banana ripens.
- The foods a person eats together can affect GI – Fiber lowers the total GI of a meal.
Low GI food –
some examples of low GI foods include:
- Non-starchy vegetables, like sweet potatoes and carrots
- Barley
- Whole grain pasta
- Bulgar
- Whole grains like whole wheat bread
- Legumes
- Lentils
- Oat bran
- Steel-cut oatmeal
- Muesli
- Brown rice
High GI food –
Foods with a higher GI include:
- Heavily processed grains, such as white rice, white bread, and white pasta
- Puffed rice
- Instant oatmeal
- Popcorn
- Starchy vegetables, such as potatoes
- Pumpkin
- Corn flakes
- Melons
- Pineapple
- Bran flakes
Glycemic Index of some common Indian Foods –
CEREALS
- Bread – 70
- Millets – 71
- Rice (white) – 72
- Wheat flour – 70
VEGETABLES
- Beans – 79
- Potato – 70
- Sweet Potato – 48
- Yam – 51
- Beetroot – 64
- sweet corn – 55
- Carrots – 35
- Pumpkin – 66
PULSES
- Soyabeans – 43
- Rajma – 29
- Bengal gram – 47
- Green gram – 48
- Black gram – 48
SUGARS
- Glucose – 100
- Fructose – 20
- Maltose – 105
- Sucrose – 59
- Honey – 87
MISCELLANEOUS
- Peanuts – 13
- Potato chips – 51
- Tomato soup – 38
- Hummus 30gm – 6
- sponge cake – 46
- Doughnut – 76
- French fries – 75
- Gatorade – 78
- Croissant – 67
- Special K cereal – 69
DAIRY
- Milk – 33
- Ice cream – 36
- Curd 36
FRUITS
- Apple – 39
- Banana – 69
- Orange – 40
- Apricots – 32
- Grapefruit – 25
- Grapes – 43
- Mangoes – 51
- Pineapple – 51
- Oranges – 48
- Strawberries – 40
- Kiwi – 58
Conclusion –
Furthermore the GI can help a person make healthful decisions about their overall diet and nutrition.
As a matter of fact People with diabetes, those trying to lose weight, and people at risk of heart disease can reap significant benefits from a low GI diet, after all the benefits extend to everyone — not just people with chronic illnesses.
Eating a low GI diet does not have to mean avoiding all high GI foods. Instead, a person’s goal should be to stay balanced over time, with a strong focus on fiber-rich foods with a low GI. A doctor or dietitian can help with planning a delicious and nourishing diet that features a wide variety of low GI foods.
If you are struggling shedding weight. You can talk to us by taking this assessment: Click here
For more information click here

