The Impacts of oats on health are enormous. Oats are a type of cereal grain belonging to the “Poaceae” grass family of plants. Its scientific name is “Avena sativa”. Oats are popular because of their high nutritional value. The grains came from edible seeds of oat grass which we eat. When we cook oats they give us a mushy texture.
Oats have enormous health benefits. They have soluble fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in rich amounts. They can help lower cholesterol and blood sugar level.
Oats are high in a fiber called beta-glucan which boosts your immunity and keeps your heart healthy. Being rich in fiber, oat keeps you full for a longer time. They also contain an antioxidant “avenanthramides”. Various studies have proven that it helps in reducing inflammation and regulating blood pressure also.
The Impacts of oats on health also depend on the type of oats:
There are many varieties of oats available in the market. They all have different nutritional values which depend upon their processing. The more processed the oats, the more the glycemic index of it. So, here are the types of oats available in the market:
Oat groats
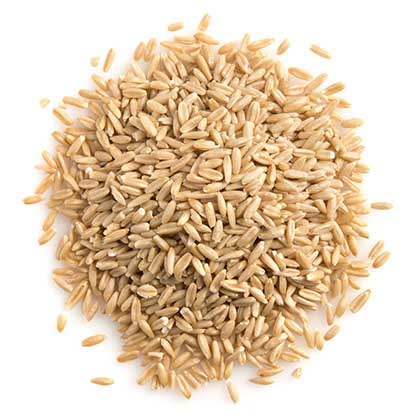

Oat grains without processing are “groats”. They retain the germ, bran, and endosperm even after removing their hull or husk by the process called “hulling”. The husk which comes out after hulling is “chaff”. Oat groats have the same nutritional value as grains. They give us a hearty and chewy texture after cooking.
There are 3 main parts of grains:
- Bran- it is the outermost part of the grain and has the highest nutritional value because of the higher dietary fiber value. Oat bran can be eaten as a hot cereal, mixed into smoothies, can be sprinkled on top of bread and other baked goods. It can help in relieving constipation and improve gut health.
- Germ- it is the core of the grain and vitamins and minerals are stored here.
- Endosperm – it is the starchy kernel of the grain which is used for milling.
Taste and texture:
- Oat groats are gluten-free so they can be eaten by people with celiac disease or gluten intolerance.
- They have a hard and chewy texture.
- Groats should be first steamed or soaked before cooking.
- They have a nutty flavor and absorb the flavor of the dish.
- You can also toast or roast the groats before adding them to a dish for a better taste.
- Also, we can use it to make pilaffs, stews, or hot cereals.
Steel-cut oats

They are also called Irish oats. When oat groats are cut into two or three smaller pieces by using a steel blade they are known as steel-cut oats. The larger the size of oats, the longer time it will take to cook. They are the least processed of all oats varieties and cook faster than oat groats but slower than rolled oats.
Taste and texture:
- Steel-cut oats are creamy and delicious.
- You can roast them before making any recipe for a better taste.
- They have good texture and flavor.
- We can use steel-cut oats for making oatcakes, smoothies, or other culinary purposes.
Scottish oats
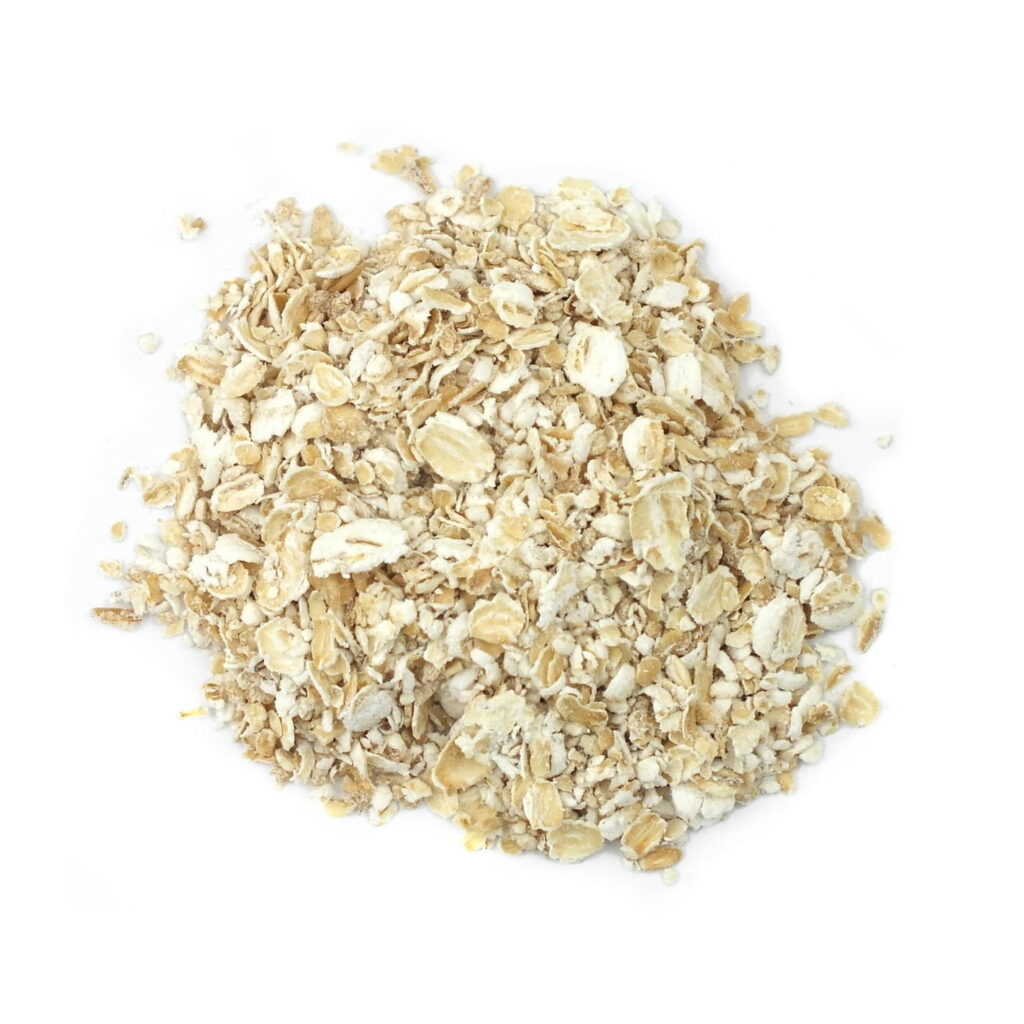

They ground with the help of stone, almost to a powder. This is a very old and traditional process. Scottish oats are also known as “scotch oats”. This type of oats get cooks a little faster than steel-cut oats and has a creamy consistency. Also, oatmeal historians consider them the “original oatmeal”.
Taste and texture:
- They are coarser than oat flour.
- It has a thick and creamy consistency which we know as porridge.
- They have a slight texture and give a fantastic taste when combined in baking recipes.
- Also, take very less time in cooking.
Rolled oats
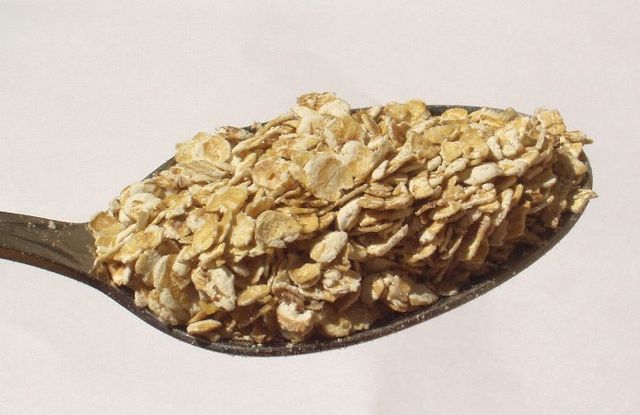

Rolled oats are made by steaming, rolling, and then flattening oat groats into flakes and then drying them. They have a chewy texture, and mild flavor, and give a creamy consistency when cooked. This process stabilizes the healthy oils in oats, so they stay fresh for a longer time and also cook faster.
We divide rolled oats into three types-
- Old-fashioned oats: The whole grains first get steam, flatten by the roller and then flake to create old-fashion oats. We use these oats in oatmeal, baked goods, and also for coating meats. It has the most texture of all three types of rolled oats.
- Quick-cooking oats: The oats are cook, dry, and cut, then roll thin more than old-fashioned oats to make quick-cooking oats. They cook faster.
- Instant oats: The oats are cook and dried before cutting and then rolled thin to make instant oats. They are the fastest-cooking oats of all types. They sometimes give gummy or mushy consistency. Instant oats are less healthy than other types of rolled oats.
Oat flour

Oat flour is the flour of oat groats which is finely grind. You can also make oat flour at home by blending or food-processing oats into fine powder. Oat flour could be use as a replacement for wheat flour. It is gluten-free.
Culinary practices:
There are so many varieties of recipes for oats. Any recipe for oats consider the type of oats. We can make overnight oats by soaking oats overnight which gives digestive and gastronomic benefits to the body. Oatmeal is made by crushing oats, which makes it easier to prepare, and cooking time is also reduced.
You can also try these different oats recipes: 31 Easy and healthy Oats Recipes which you can enjoy at any time of the day
Whereas, rice is one of the most popular cereal grains in the world. You can not consume rice raw because it may have bacteria, dirt, or other harmful substances. Soup, dessert, and pudding are the products of rice. Rice doesn’t take a long time to cook.
Wheat processing occurs to make multiple wheat products like flour, semolina, and bran. Their processing is done to make the dough, bread, pasta, or any breakfast component. Beer and whisky are also products of wheat.
Price comparison:
Wheat and rice are cheaper than oats. However, the price may vary in different parts of the world and also on the type of processing done on oats, rice, and wheat. The Impacts of oats on health are soo many that their price does not matter.
Shelf life:
They all have a longer shelf life if stored properly. We should store it in a dry place.
Nutritional comparison of oats, rice, and wheat:
Diet and weight loss-
Oats can promote a healthy and well-balanced diet. The Impacts of oats on health are soo many. Taking oats in breakfast can boost your energy. Overnight oats with fruit and nut is a wonderful option for breakfast.
Rice can help in weight loss if taken in moderation. It makes the person feel full faster, so calorie consumption is less. Rice is a major cereal in India and is widely get consume in Asian cuisine.
Wheat contains a major protein called “gluten” which makes it adhesive and sticky when combined with water. It helps in pasta and bread making. So, people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity or on a gluten-free diet cannot consume wheat. They can take it out as a replacement for wheat.
2. Keto diet:
Oats, rice, and wheat all are high in carbs. Therefore, we should not consume them on the keto diet. However, some foods have less of their quantity . We can eat them Consider the content of them before eating.
The Impacts of oats on health:
The Impacts of oats on health are the following:
- Role in digestion – oats reduce the risk of diverticulitis and lipid absorption which shows a positive effect on overall metabolism oats also make intestinal microflora great by improving its performance. Wheat also reduces the risk of diverticulitis if eaten with husk and bran.
- For diabetic patients – wheat and oats consumption reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes. Also, they keep blood glucose and triglyceride level in control. Rice is not as good as wheat and oats for diabetic patients because it has a high glycaemic index. So, we can eat it moderately.
- Heart health – oats lower serum cholesterol and blood sugar level which lowers the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. Eating rice in moderation is not harmful to heart health.
- Cancer – beta-glucans found in oats show anti-carcinogenic properties against lung cancer cells. Whereas, wheat also reduces the risk of developing colon cancer.
- Celiac disease – celiac disease is sensitivity to a protein called “gluten” in people. Oats and rice do not contain gluten which is present in wheat. So, they can easily consume by people who have celiac disease, gluten sensitivity or are on a gluten-free diet. People with celiac disease should not consume wheat.
Nutrient comparison in oats, wheat, and rice
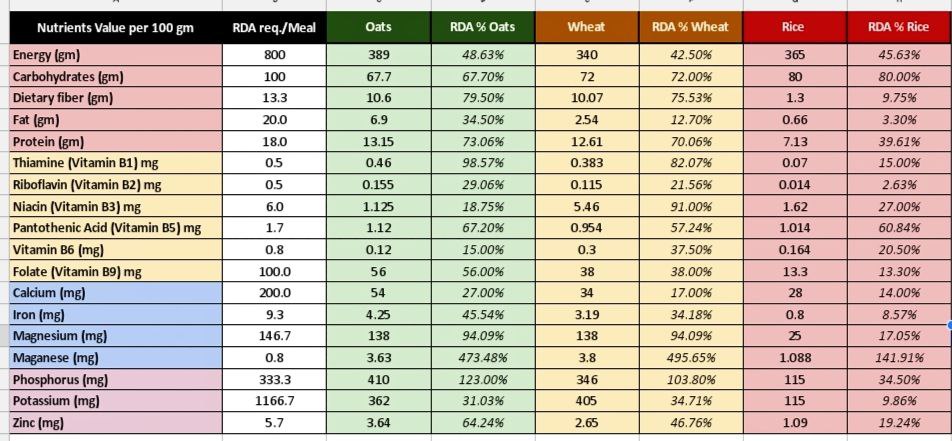
Carbohydrates present in oats is 67.7 gm, in wheat is 72 gm and in rice is 80 gm which shows oats give fewer carbohydrates in comparison to wheat and rice despite giving maximum energy. Oats have 10.7 gm of dietary fiber, wheat has 10.06 gm and rice has 1.3 gm. In dietary fiber also oats have the maximum quantity. It can help in weight loss. Oats are very rich in protein. They have 13.15 gm of protein whereas, wheat has 12.6gm, and, rice has 7.13gm. So, by these points, we come to know that oats are better than rice and wheat in terms of carbohydrates, protein, and fiber.
Then, we see oats have thiamine 0.46mg of, wheat has 0.383mg of, and rice has 0.7mg which is also a good quantity. Riboflavin in oats is 0.155 mg, wheat has 0.115mg and rice has 0.014mg. Oats have the most riboflavin in comparison to wheat and rice and, riboflavin is very important for body growth. Niacin is 1.125 mg in oats, 5.46 mg in wheat, and 1.62 mg in rice. So, niacin is higher in wheat. Niacin is important to keep our nervous system, digestive system, and skin healthy. Pantothenic acid and folate quantity are also higher in oats and which makes oats better in terms of vitamin content than wheat and rice.
Now, we see calcium is 54 mg in oats, 34 mg in wheat, and 28 mg in rice. So, oats have the highest calcium quantity than wheat and rice. Calcium is very important for bones. Iron is high in oats in comparison to oats. The quantity of iron in oats, wheat, and rice is 9.3mg, 3.19mg, and 0.8 mg respectively. Magnesium is present in equal amounts in oats and wheat but less in rice. Manganese is higher in wheat which is 3.8 mg in wheat, 3.63 mg in oats, and 1.088 mg in rice. So, oats have almost the same quantity of manganese as wheat. By comparing these terms also we get to know that oats are better in comparison to rice and wheat.
Phosphorus in oats is 333.3 mg, 346 mg in wheat, and 115 mg in rice. So, wheat is better in phosphorus quantity. Then, we see potassium is 362 mg in oats, 405mg in wheat, and 115 mg in rice. So, wheat is also higher in the potassium range. After that, we see zinc is 3.64 mg in oats, 2.65 in wheat, and 1.09 mg in rice. So, the quantity of zinc is higher in oats. Zinc is very important for boosting your immunity and metabolic function in the body.
If you are facing issues in dropping your weight, please take this free-body type assessment: Click here

